
05 Oct 3 Practical Steps for Improving Your Cybersecurity Defence
Intro
In this article, we’ll review Aus Advantage’s top 3 practical steps for improving your cybersecurity defence, based on our experience with SMBs in Australia.
As Australian businesses embrace the next step of the digital age with open arms, the adoption of cloud technologies has witnessed an exponential surge. These technologies have revolutionised the way businesses operate, driving unseen levels of productivity, collaboration, and flexibility; however, this silver lining doesn’t come without its cloud (pun intended).
With an increased number of people accessing online services globally and with IT literacy only increasing, the surface area for potential threats has drastically expanded, inadvertently amplifying online exposure for businesses. A telling snapshot from the ACSC latest Annual Cyber Threat Report highlights the magnitude of the challenge.
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC – Part of the federal government’s Australian Signals Directorate) received over 76,000 cybercrime reports in 2022, an increase of nearly 13% from the previous financial year.
This equates to one report every 7 minutes, with ransomware remaining the most destructive cybercrime to SMEs, and Business Email Compromise (BEC) being the most used attack vector, costing the economy over $98 million last financial year. This rampant uplift in cybercrime is costing Australian businesses $64,000 in losses per incident. An increase of 14% from the previous year. Source: https://www.cyber.gov.au/about-us/reports-and-statistics/acsc-annual-cyber-threat-report-july-2021-june-2022
These figures are a sobering reminder of the evolving cyber threat landscape and the pressing need for businesses to bolster their cybersecurity defences. In light of this, we have listed 3 practical steps that you can take to immediately improve your cybersecurity defence.
Step 1 – Multi Factor Authentication
MFA is not a new technology. You likely already utilise it within your business. The question is: Are you using it in the right way, and have you applied it everywhere?
While you might be familiar with text-based (SMS) and voice recognition as a method of MFA, it’s worth noting that these methods are now considered insecure. Spoofing mobile numbers has become a trick of the trade for cybercriminals, especially in targeted attacks against high-profile individuals like CEOs, CFOs, and people in positions of power within a company.
Even the more modern push-based MFA services which utilise apps such as Microsoft Authenticator and Google Authenticator to generate codes or send popup style notifications to your mobile have their weaknesses.
In recent years, attackers have learned that repeatedly sending MFA requests to a account will likely end in the person clicking accept on the prompt either by accident or through a concept called MFA Fatigue.
The bottom line? Not all MFA is created equal and ensuring you use the appropriate protection mechanism that’s available to you is the first critical step. Below is a list of MFA methods ranked in order of security.
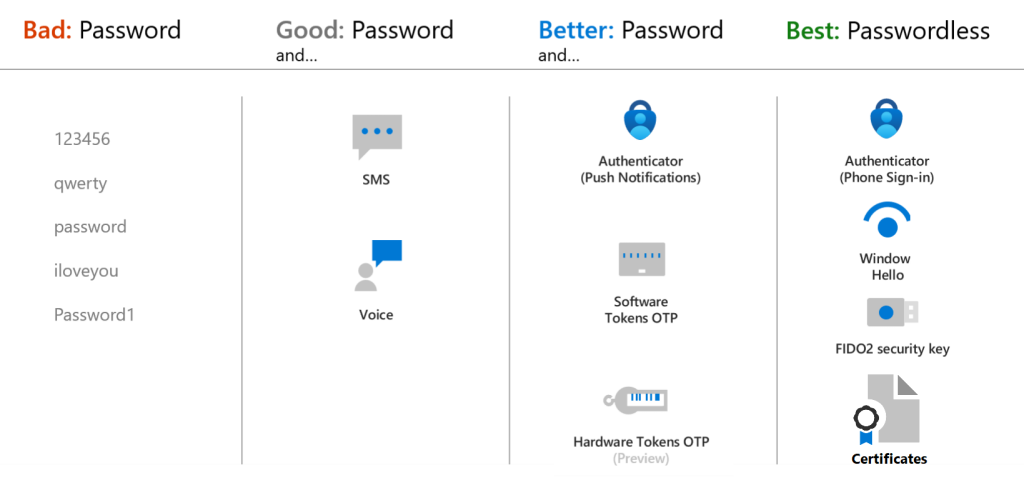
Were possible, leverage advanced condition-based identity management services such as Microsoft’s Conditional Access Policies to only allow logins from approved locations, or approved company devices that have been properly secured, and ensure number matching is enabled to reduce exposure from MFA fatigue.
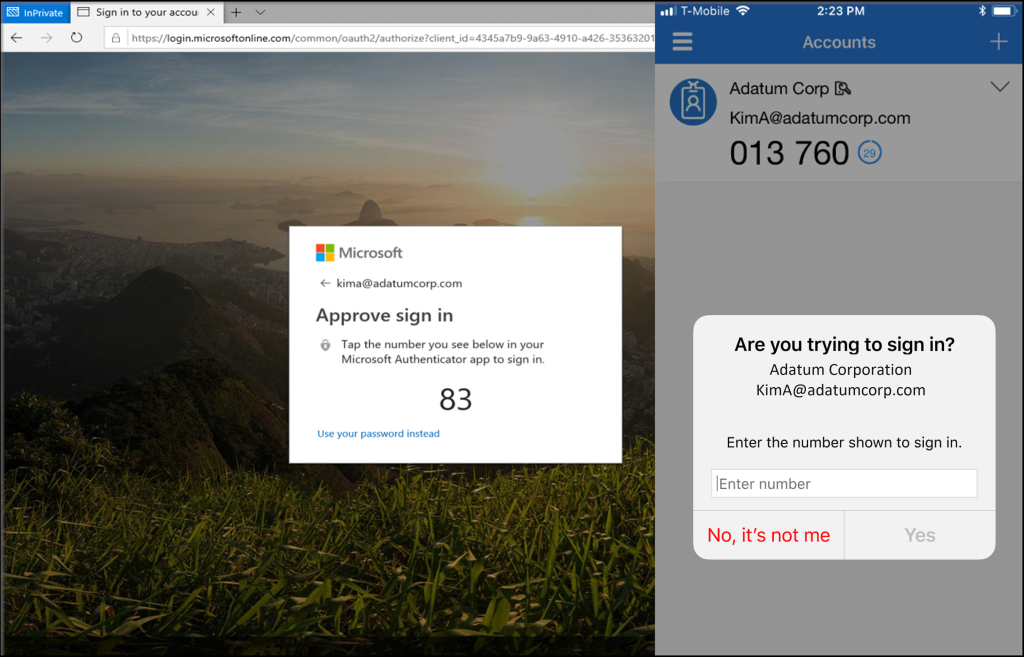
This can be a lot for any business to address, so start small and begin with the essentials. Catalogue all your logins and integrate the best MFA method across the board. But remember, every new security layer impacts company culture. Changes, even those meant for protection, can be met with resistance. It’s crucial to foster an understanding that these measures are in place to shield the company and its employees from potential threats. Tread thoughtfully, ensuring employees aren’t overwhelmed, but rather, empowered.
Step 2 – Educate Your Staff
Your staff are often the first line of defence, and their awareness and preparedness play a pivotal role in defending against threats. It may come as a surprise, but unfortunately humans are the #1 cause of cyber security breaches:
- 85% of data breaches involve the human element
- Negligent employees cause about 62% of security incidents
- 82% of leaders see a greater risk of insider threats if under a hybrid working model
By educating your staff on what to look out for, you can drastically reduce your chances of becoming a victim of cybercrime, and quickly too.
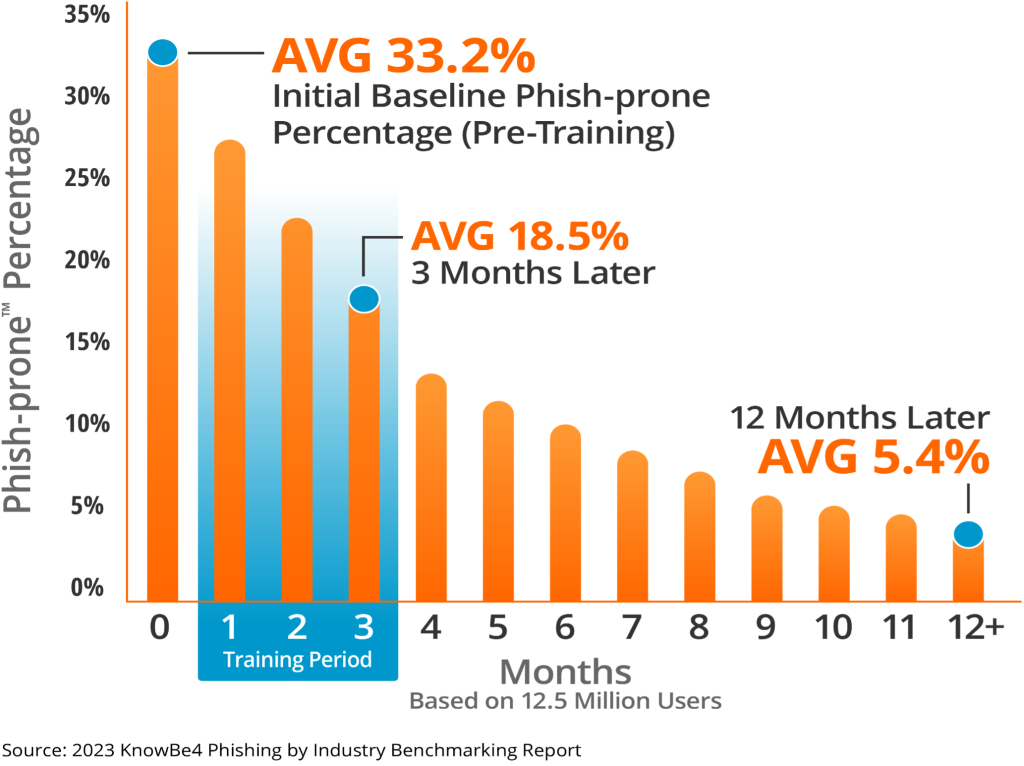
With the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, traditional once-a-year training modules are insufficient. Instead, proactive approaches like simulated phishing tests are emerging as game-changers. By using varying complexity in these tests, businesses can accurately gauge their team’s readiness and response against real-world phishing attempts.
Products like Usecure provide these services, giving a realistic experience and immediate feedback to users.
Implement targeted campaigns that don’t just aim to catch employees out but rather highlight areas of improvement. Once these areas are pinpointed, the company can assign specific training modules to enhance the team’s knowledge in those segments. This method of targeted training ensures that your staff isn’t just aware but is also continuously evolving in their cybersecurity practices.
If you’re interested in finding out how well your team are educated, and who is likely to click on malicious links, sign up for a free email phishing test and domain security scan.
Sign up for a free domain security scan and simulated phishing test with Aus Advantage & Usecure.
Step 3 – Review Your Backup Strategy
We’ve all been there – thinking that it’s something to worry about “later”, but the truth is, backups are the silent guardian every business desperately needs but are typically only recognised when things go wrong.

Now, let’s wind the clock back a bit. If you’ve been in business for a while, you might remember the whir of tape drives doing their backup magic and the need to take those tapes home each night… and occasionally forgetting to do so.
But times have changed, and over the last decade the cloud has swept in and completely changed how we secure technology. No more tapes, just the vast, expanse of the cloud. And while that’s fantastic in many ways, it comes with its own set of challenges.
Here’s a little secret that often gets missed: just because you’ve stored something on popular platforms like Microsoft SharePoint, OneDrive, or Google Workspace, doesn’t mean it’s backed up. If your files get corrupted, accidentally deleted, or worst-case scenario, held hostage by ransomware, there isn’t a magic “undo” button within these cloud platforms.
Deploying a comprehensive backup and disaster recovery strategy isn’t just a good idea, its basic business hygiene, and failing to properly protect your business could mean starting from scratch should the worst happen.
The best way to start tacking this problem is to start by identifying where all your business’ critical data resides. This could be your email, cloud file storage, a file server, CRM, or finance solution.
The next step isn’t to start backing up, it’s to understand your specific backup requirements. How long can you go without the most recent copy of your data, how often do you need to take a backup (RPO), and how quickly do you need to be able to restore (RTO)?
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) describes the interval of time that might pass during a disruption before the quantity of data lost during that period exceeds the Business’ allowable threshold or tolerance. For example, if the last available good copy of data upon an outage is from 18 hours ago, and the RPO for this business is 20 hours then we are still within the parameters of the Business Continuity Plan’s RPO.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the duration of time and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster in order to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in continuity.
So how do you calculate RPO?
There are many factors that impact the RPO for your business and it will vary with each application. Below are some of the factors that can affect RPOs:
- The maximum tolerable data loss for the specific company
- Industry-specific factors, such as businesses dealing with sensitive information such as financial and health records
- Data storage options, such as physical files versus cloud storage, can affect the speed of recovery
- The cost of data loss and lost operations
- Compliance schemes include provisions for disaster recovery, data loss, and data availability that may affect businesses
- The cost of implementing each disaster recovery solution
Once you fully understand where your data exists, what platforms it sits on, how often you need to backup and how quickly you need to restore, you can begin deploying the appropriate solutions.
Backups come in many forms. They can be as easy as the tape drive backups of 10-years ago, or as simple as taking a manual export from your CRM once a week. Cloud provider like AFI offer easy to deploy cloud-to-cloud backup and restoration services for Microsoft 365 SharePoint, OneDrive, Email and Teams data.

Now that you have your data protected, it’s time to schedule those reoccurring calendar entries. Business change: they grow, shrink and morph over time, and with that the technology used within the business changes.
It’s important that your backup and disaster recovery strategy is reviewed at least once a year to ensure all data remains protected, and your RTOs and RPOs are still valid.
Lastly, test your backups at least yearly, but as often as you can or are required to do so. It doesn’t matter if your backup reports show a success message. An untested backup may as well be no backup.
Conclusion
In conclusion, all the steps mentioned above play a critical role in protecting your business from damage and improving your overall cyber resiliency, but they are by no means the complete picture.
The above mentioned topics are fundamental areas of IT security and for a complete list, we recommend following a structured cybersecurity framework like the ACSCs Essential Eight to provide a comprehensive overview for all areas of concern and to provide context for each change.
It’s worth noting that the above mentioned steps are now foundational requirements for obtaining or renewing cyber liability insurance policies. You can read our previous blog about how cyber insurance policies can easily be invalidated by not deploying essential security mechanisms.
The steps above can be a lot for any business to manage, so while we recommend everyone educates themselves on best practices, we also recognise you might need a helping hand when navigating these waters.
For expert and impartial cybersecurity tailored for SMBs, speak with the team at Aus Advantage.
